Tail gas treatment
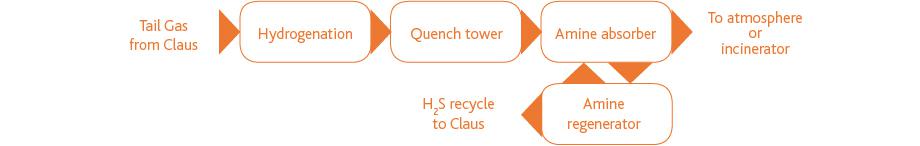
The tail gas treatment (TGT) process converts sulfur vapor and sulfur dioxide (SO2) contained in the tail gas from the Claus process to H2S, absorbs it in the absorbing solution (amine), and returns it to the Claus process, thereby achieving a high rate of sulfur recovery.
Processes:
Products:
Requirements:
The TGT is typically designed to deliver a gas containing between 10 and 250 ppmv of residual H2S, which is emitted into the atmosphere or incinerated. The precise amount will depend on the environmental legislation or general plant environmental targets. Often an incinerator is installed before emission in order to oxidize the H2S to the less hazardous SO2.
Challenges
The removal requirements for a tail gas treatment unit are particularly challenging because of the extremely low pressure and the presence of CO2, since CO2 absorption needs to be minimized. MDEA-based solvents are preferred because of the inherent selectivity of a tertiary amine like MDEA, which favors H2S absorption over CO2.
Eastman’s answer
Eastman AdapT solvents are formulated to maximize the selectivity beyond the performance associated with unformulated MDEA.
The use of Eastman’s amine, featuring deep sulfur removal, achieves more than 99.9 percent sulfur recovery in the sulfur removal block.